POSTNATAL CARE AND POSTPARTUM EXERCISES | HDS
POST NATAL CARE or PNC is specialized care for the mother that begins immediately after delivery, up to a period of roughly eight weeks.
Systematic examination of the mother and baby and appropriate advice given to the mother during postpartum period.
The first postnatal examination is done and the advice is given on discharge of the patient from the hospital.
The second routine postnatal care is conducted at the end of the 6th week postpartum.
Aims & Objectives –
- To assess health status of the mother, especially medical disorders like diabetes, hypertension should be reassessed.
- To detect and treat at the earliest any gynecological condition arising out of obstetric cause eg fistula, perineal tear, inversion of uterus.
- To note the progress of the baby including the immunization schedule for the infant.
- To impart family planning guidance.
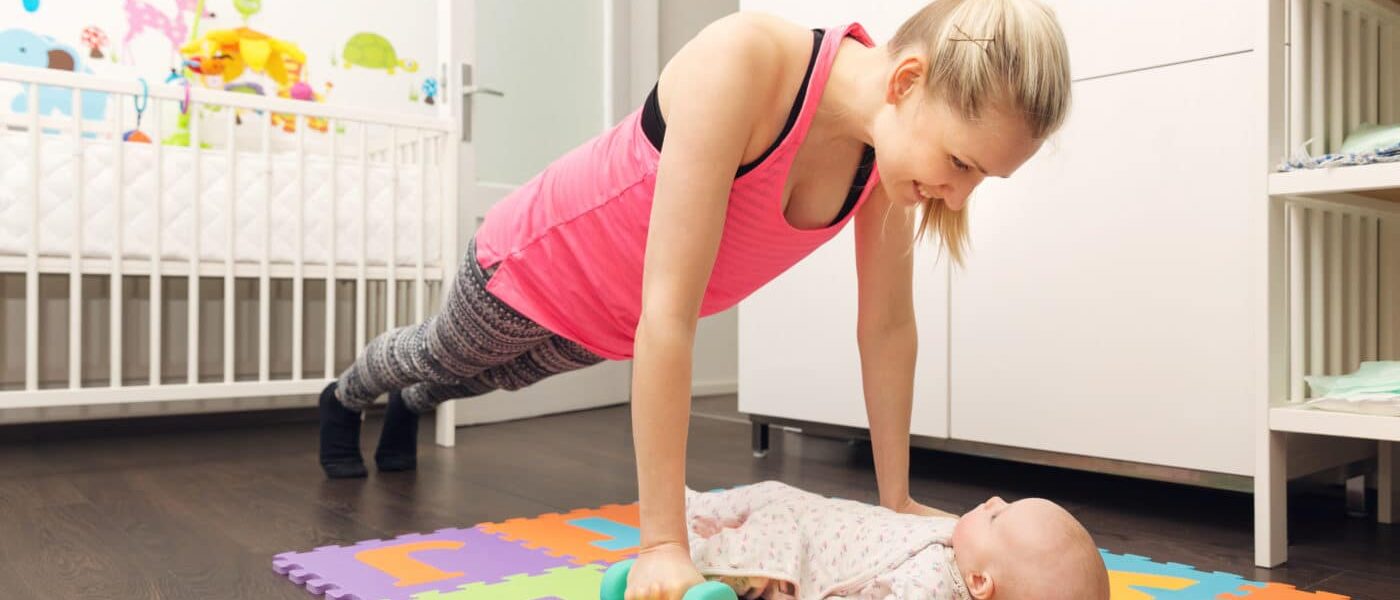
Physical activity should be resumed without delay. Sexual intercourse only after lochia has stopped (after 6 weeks).

The objective of post partum exercises are :
- To improve the muscle tone, which are stretched during pregnancy and labour especially the abdominal and perineal muscles.
- To educate about correct posture to be attained when the patient is getting up from her bed. This also includes the correct principle of lifting and working positions during day to day activities.
Advantages are –
- To minimize the risk of puerperal venous thrombosis by promoting arterial circulation and preventing venous stasis.
- To prevent backache.
- To prevent genital prolapse.
Initially she is taught breathing exercise and leg movements lying in bed. Gradually she is instructed to tone up the abdominal and perineal muscles. The exercise should be continued for at least 3 months.
The common exercises prescribed are –
- Kegel’s exercise – strengthened the perineal muscles. Can be advised for patients with menopausal age group, with stress urinary incontinence, all cases of prolapse, patient who have delivered.
- For abdominal muscles – The patient has to lie in dorsal position with the knees bent and feet flat on bed. The abdominal muscles are contracted and relaxed alternately and the process is to be repeated several times a day.
- For back muscles – Patient has to lie on her face with the arms by her side. The head and shoulders are slowly moved up and down. The procedure is to be repeated 3-4 times a day.
Worked By – Dr. Nazia Ansari (BHMS)