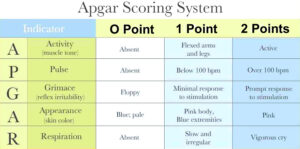
The APGAR Score is a simple, rapid method to assess the health and vitality of a newborn immediately after birth. It evaluates five key criteria; each assigned a score from 0 to 2. The total score ranges from 0 to 10 and helps guide initial care and interventions for the newborn.
Timing of APGAR Assessment –
- 1 minute after birth : Reflects the baby’s initial adaptation to extrauterine life.
- 5 minutes after birth : Provides insight into how well the baby is progressing. If the score remains low, further assessments may be done at 10 and 15 minutes.
Interpreting the APGAR Score –
| Score | Interpretation | Action |
| 7 – 10 | Normal, healthy baby | Routine care |
| 4 – 6 | Moderately depressed | Some resuscitation (eg oxygen, stimulation) may be needed. |
| 0 – 3 | Severely depressed | Immediate resuscitation and advanced care required |
Clinical Significance –
The APGAR Score provides a quick snapshot of a newborn’s health, but it is not used to predict long – term outcomes. It helps guide immediate interventions :
- Low Score ( especially < 4 at 5 minutes ) may indicate the need for immediate resuscitation or further evaluation for underlying conditions ( eg. Birth asphyxia ).
- Improving Scores between 1 and 5 minutes suggest the newborn is responding well to interventions.
Important Considerations –
- The APGAR Score is not a definitive diagnostic tool but a clinical guide.
- For babies born prematurely or with known conditions, modifications may be required in interpretation.
- Ongoing Monitoring : Even if the score is good, continuous monitoring is important, particularly in high risk cases.
Additional Care Guidelines –
- Immediate Skin to Skin contact : If the baby has a normal APGAR score, encourage skin to skin contact with the mother.
- Neonatal Resuscitation: Be prepared to initiate resuscitation if the score is < 4.
- Communication with Parents : Explain the significance of the APGAR score in simple terms, especially if interventions are needed.
Worked By – Dr. Nazia Ansari (BHMS)